Stay Secure, Stay Informed: A Look into Deceptive Practices Targeting Bank Customers
In the current landscape of digital banking, a concerning trend has emerged that puts account holders at risk of falling victim to sophisticated cyber scams. Banks are now urging their customers to update their account information by submitting their National Identification Number (NIN), a move aimed at enhancing security measures. However, this well-intentioned process has inadvertently opened the door for threat actors specializing in Business Email Compromise (BEC) and phishing scams to exploit unsuspecting users.
Phishing Meets Timing
These malicious actors have been quick to capitalize on the situation by setting up fake or replica versions of corporate banking websites to deceive individuals into divulging their personally identifiable information. By mimicking the legitimate interfaces of banks, these fraudulent websites trick users into entering sensitive data, such as login credentials, token codes, and NINs, under the guise of security compliance.
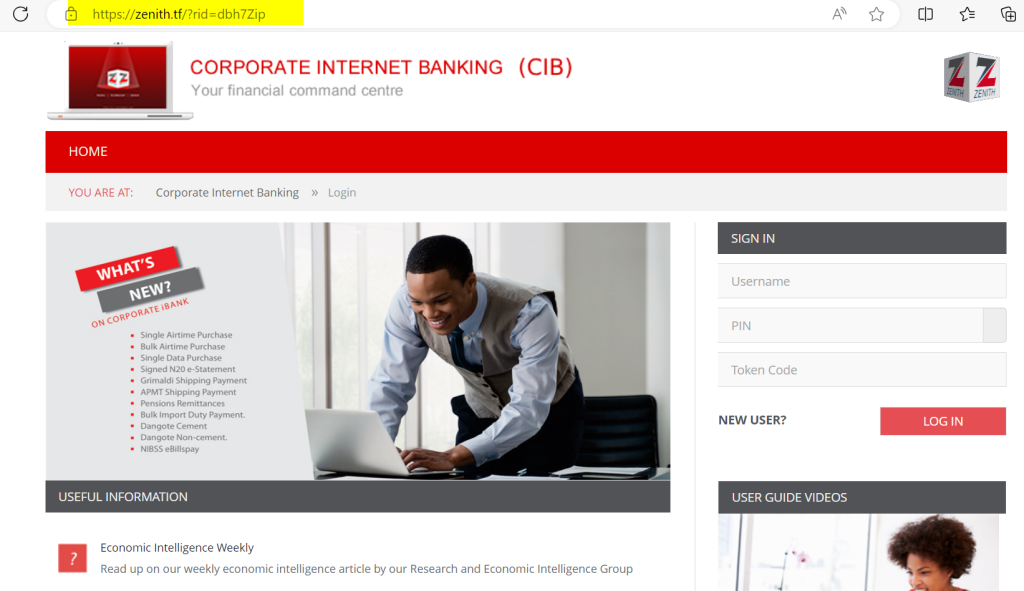
Recently, our vigilant team stumbled upon a server that had been specifically configured to facilitate these deceptive practices. Recognizing the imminent threat posed by these fraudulent activities, we undertook a thorough investigation to uncover the indicators of compromise (IoC) associated with such malicious endeavours.
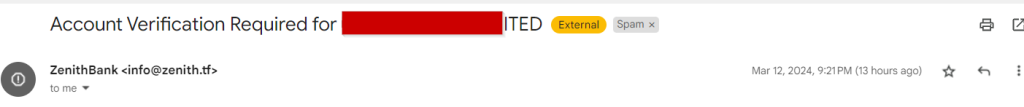
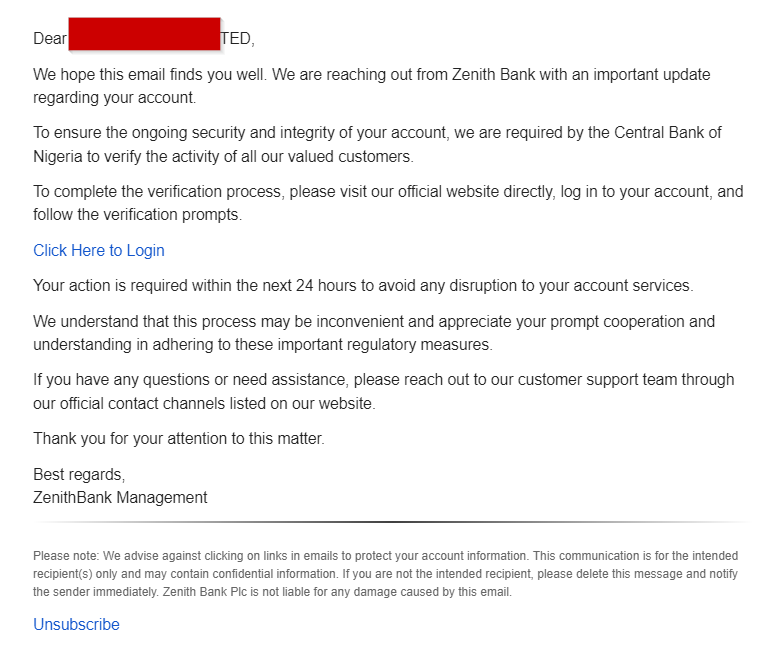
As responsible digital citizens, it is crucial for all bank customers to remain vigilant and cautious when navigating online banking platforms. To safeguard against falling prey to these nefarious schemes, users should exercise due diligence by verifying the authenticity of banking websites, scrutinizing email communications for signs of phishing attempts, and refraining from sharing sensitive information unless absolutely certain of the legitimacy of the request.
By staying informed and proactive in our cybersecurity practices, we can collectively combat the insidious efforts of threat actors seeking to exploit unsuspecting individuals. Remember, when it comes to safeguarding your personal information in the digital realm, vigilance is key.
Technical Analysis of the Phishing Page
The phishing page seems to be an exact copy of the original login page, down to the customer support widget at the bottom.
But they only seem like an exact copy at first glance, the difference between the phishing page and the actual login page, purely by a matter of the goal the attackers are trying to achieve, will always be the form.
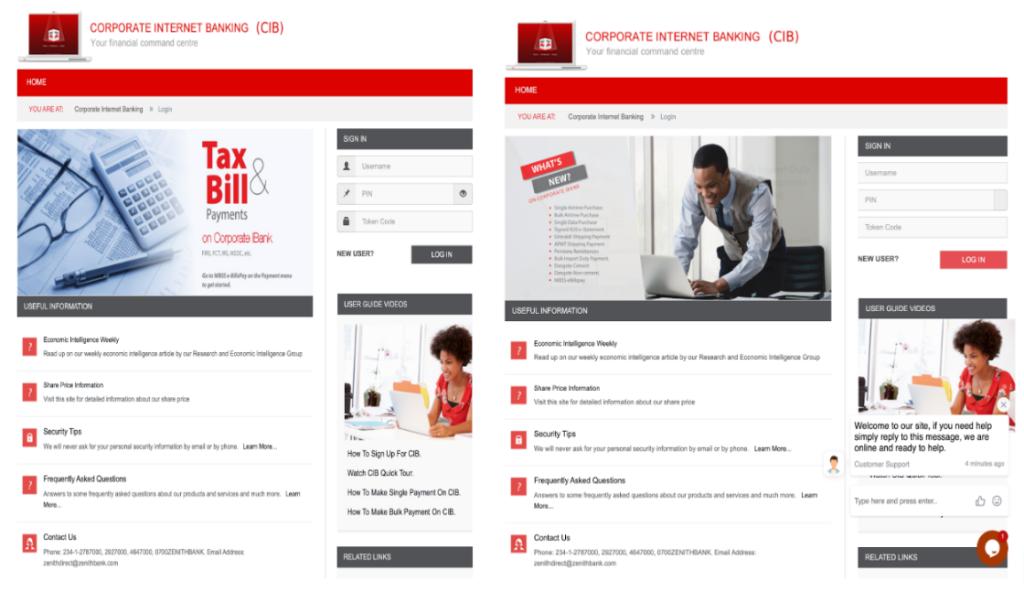
Visually, the only difference is the icons but this indicates that the code for the form itself has been altered. To test how the two forms work, we’ll attempt logging in using an alter ego. “Adams Chinedu“
After “Logging in”, the form will send the data to the server and this is how we get the endpoint where all the data is sent.
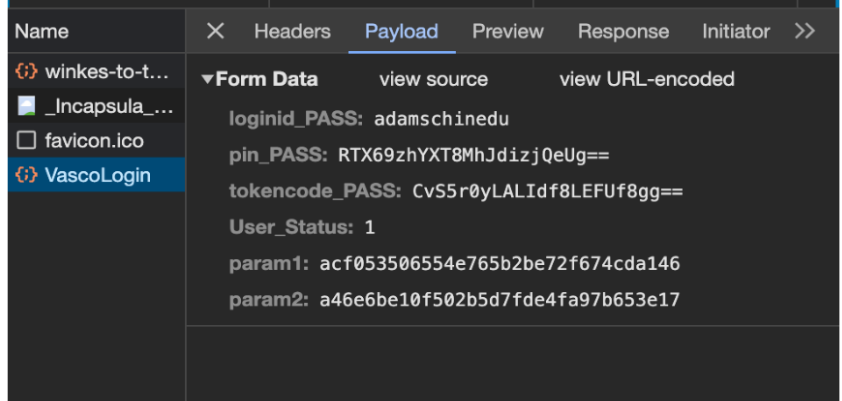
The legitimate Zenith Bank form passes the user, then pin and token as encoded values along with what I suspect to be csrf hashes.
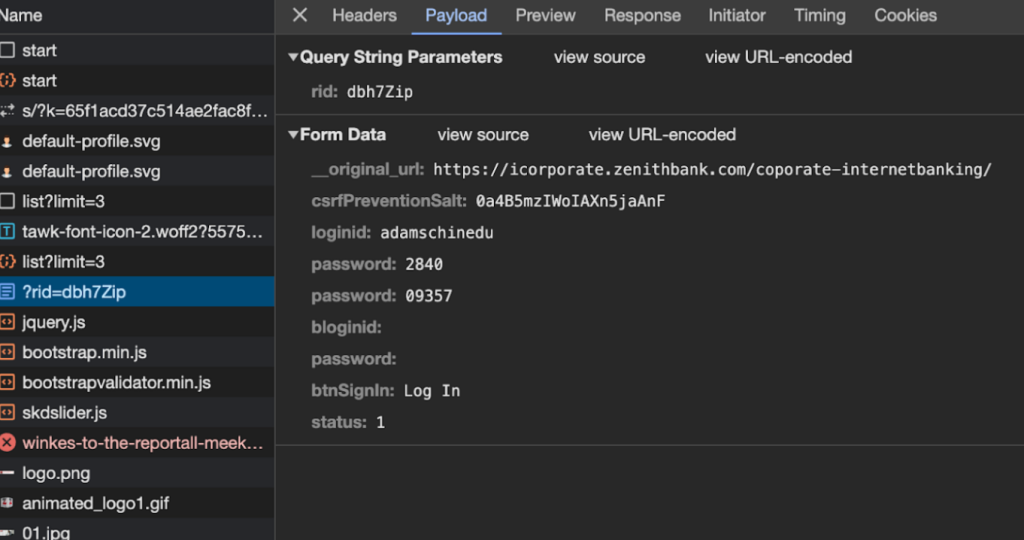
The phishing page on the other hand takes the original url of the page it is pretending to be (probably to use as a target url when the details are entered)
The existence of this variable also alludes to this page being set up by a tool, since if it were a one-off, the developer would have hardcoded a value in the code instead.
The request also passes on the rid query parameter that can be seen in the url bar. This probably is an identifier for the target that received the phishing link.
Indicator of Compromise
https[:]//zenith[.]tf/?rid=dbh7Zip
188.114.96[.]2
info@zenith[.]tf
https[:]//zenithbankplc[.]zom.ng
188.114.97[.]0, 188.114.96[.]0, 2a06:98c1[:]3120::c
https[:]//zenith[.]com.pt/?keyname=ewCgchx
https[:]//secure[.]zenith.it[.]com/coporate-internetbanking/RVFFA5W
secure[.]zenith
it[.]com
104.21.43[.]207
zenith-support@server7-nigeria[.]xyz
server7-nigeria[.]xyz
https[:]//zenith[.]com[.]pt/?keyname=9JCqtKX
https[:]//z[.]plc[.]pm/?keyname=NzYuQkM
https[:]//zenith[.]tf/?keyname=bqRqrIw
https[:]//icorporate[.]zenithb[.]ankplc[.]com/NSZ1equ

Leave a Reply