How Legacy Systems have become Soft Landing for Threat Actors.

A legacy VPN system gave access to the ransomware gang that breached Colonial Pipeline and made them pay a whooping sum of $4.4 million dollar worth of Bitcoin ( 75 Bitcoin at the time of payment).
How are you handling Legacy systems in your organization today? Are they given prioritiy? or we don’t even care about them anymore. Reports have shown that every security team has to pay special attention to those devices that are running legacy software and hardware because of their ease of compromise
What Legacy Systems are?
In computing, a legacy system is an old method, technology, computer system, or application program, “of, relating to, or being a previous or outdated computer system,” yet still in use. Below are some compelling reasons organizations may be keeping a legacy system;
- The system works satisfactorily, and the owner sees no reason to change it.
- The costs of redesigning or replacing the system are prohibitive because it is large, or complex.
- Retraining on a new system would be costly in lost time and money, compared to the anticipated appreciable benefits of replacing it (which may be zero).
- The system requires near-constant availability, so it cannot be taken out of service, and the cost of designing a new system with a similar availability level is high. Examples can be systems to handle customers’ accounts in banks, computer reservations systems, energy distribution (power grids), nuclear power plants, and military defense installations.
- The way that the system works is not well understood. Such a situation can occur when the designers of the system have left the organization, and the system has either not been fully documented or documentation has been lost.
Why this is a problem?
Looking at most parastatal, agency, and ministries of the government today, we have seen so many legacy software and hardware in use. Many are lucky to have not experienced ransomware incident due to the kill switch that exists (especially for WannaCry), preventing their file from getting encrypted.
The Span
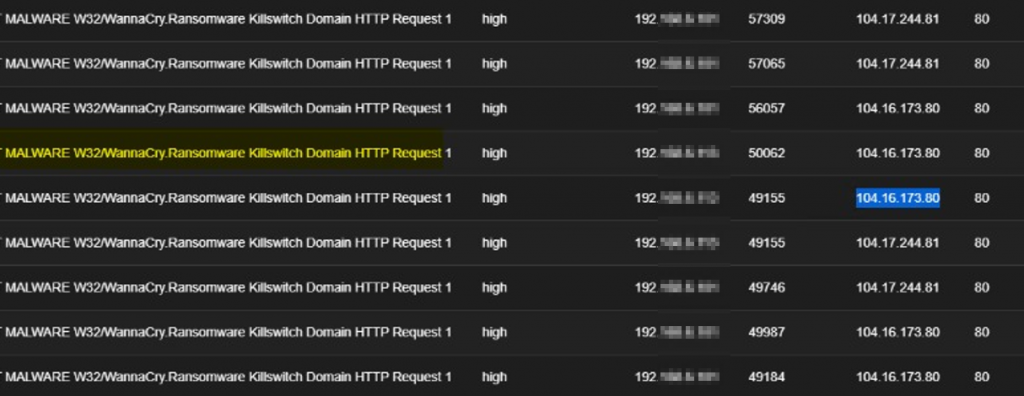
In one of our engagements, we observed, after deploying our next-generation Security Information and Event Management System (ng-SIEM) that a whole network has been compromised with Wannacry involving different workstations in departments within the organization. This engagement revealed that mostly Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 are Operating systems that dominated the network, giving the attacker the leverage to move around on port 445 (SMB) which hosts the known vulnerability for the WannaCry Ransomware. Not only this but enormous crypto miners were also detected on tens of workstations within the organization’s network, consuming network bandwidth and system resources. What is surprising is how much of these unsupported versions of the Windows Operating systems (Reached End of Life) from Microsoft dominated a network in 2021. Another question would be how has audit around Information System & Security Management been missing them, for many that claimed to be certified.
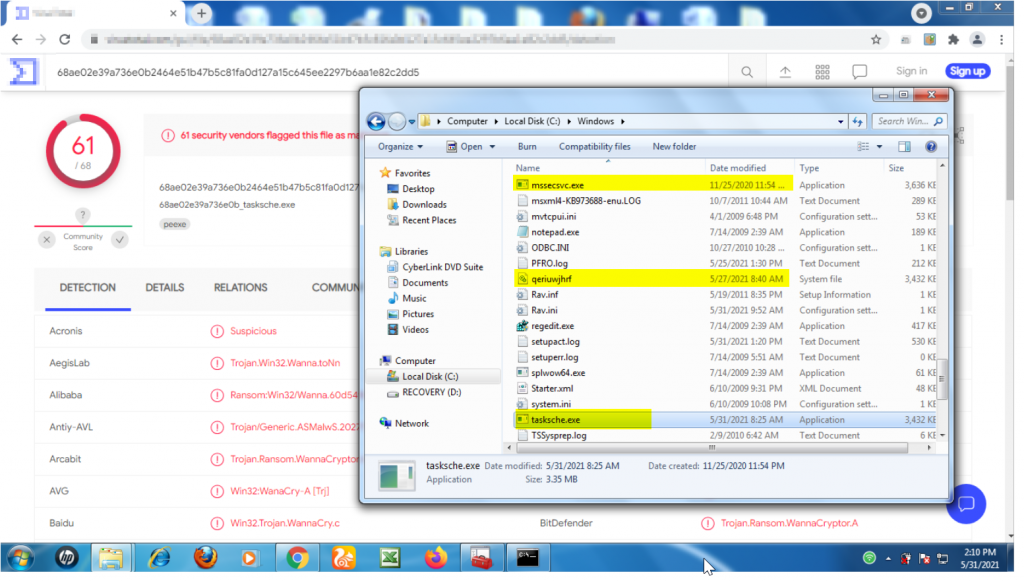
At this point, our team cannot but ensure we bring them up to speed by clearing all threats and recommending replacement old versions of Operating Systems and applications was implemented in the shortest time possible, while the endpoint security layer was activated for all workstations to ensure fail-safe opportunity at all layers.
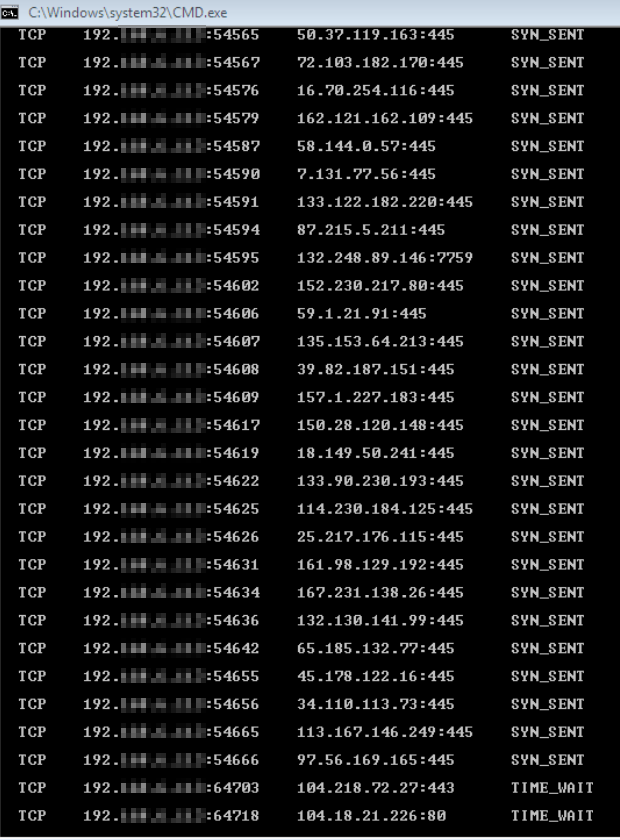
For IT team and employees, so long they can still use their systems, unknowingly sitting on a time bomb that may tick any time when it involves one of these new variants of Ransomware groups wreaking havoc across the world like Avvadon, Conti, Darkside and others. And in many other cases APT ( Advanced Persistent Threat) actors, where the focus is data exfiltration, collection of servers for botnets, crypto-jacking, users credential’s compromise, and dark web data leakage.
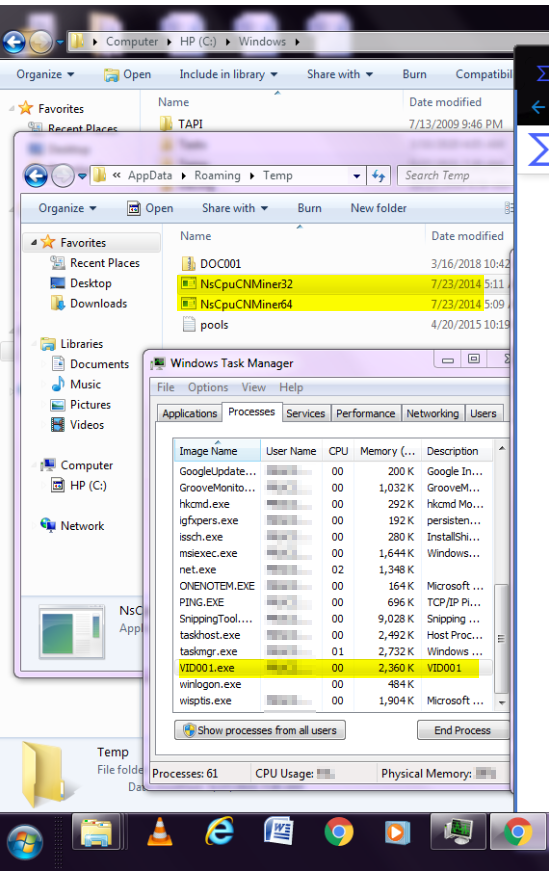
How do you advise an organization to move away from Apache services that have been installed for almost a decade without an update or other security routines due to limitations of web applications not built to scale? For many that argued how they cannot just throw off these legacy systems, a use case where special consideration in term of security is not even in place to protect those applications and hardware covered on this list can consider hardening, use of DMZ, continuous monitoring and many other blue techniques that can further help assure the protection of affected systems and applications.
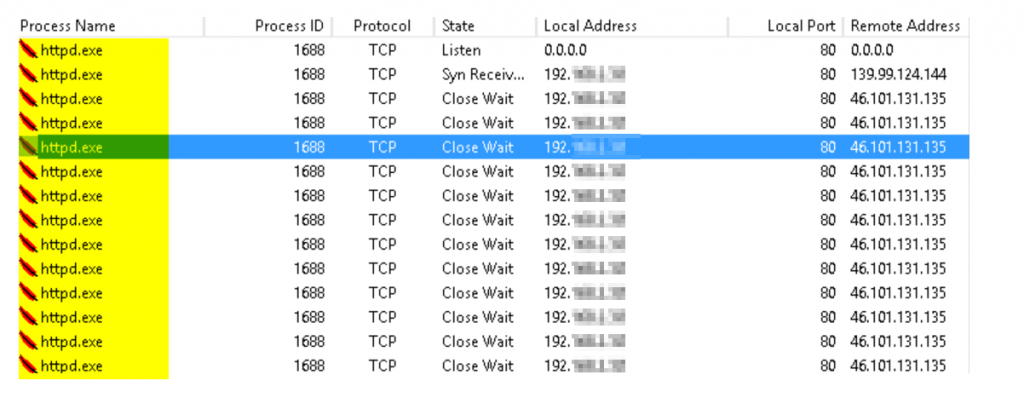
We noticed that the core objective while keeping most of those old applications is to keep ensuring functionality while ruling down on security ( the slogan is; it is working and that is how we have been using it). What many managers of these old applications met are documentations on how to keep it running to support organizational needs; hence, they are ignorant of the architecture of the systems and how to scale them up to work in the latest environment.
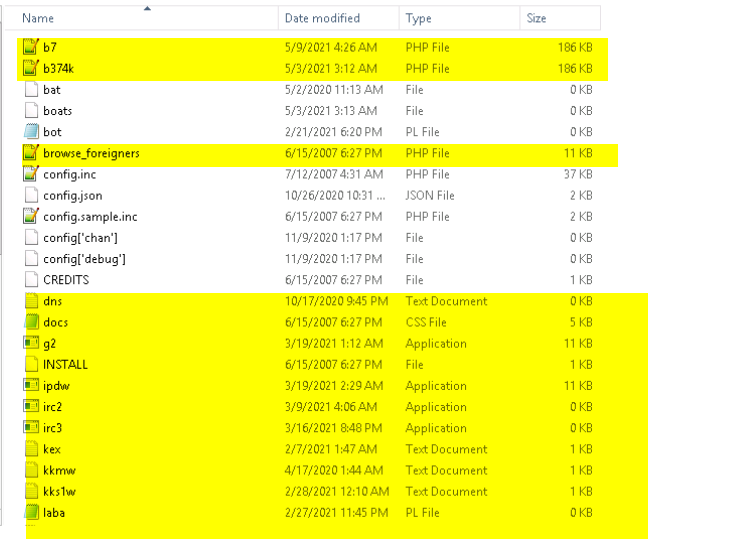
Some organizations are already on the way out of migrating from these old systems by rebuilding their applications to fit into more recent environments in term of operating systems and underlying hardware requirements so as to keep out security threat from the organization. They are also doing it for the speed and other users need which may not be initially featured in the old applications. We advised that security should be part of what to be considered and should be part of the plan from the onset in this new rework, by subjecting them to application testing, code review right before deploying into production and afterwards.
Important to note here is, while we continue to preach that organizations should move away from legacy systems as much as they can, that doesn’t mean the latest systems and technologies are not vulnerable. Especially when processes to keep them stay secured are not in place in the organization, which is the gap our team at CyberPlural come to bridge. For many businesses that are still thinking the focus is on the big names, and government have to start putting measures in place to ensure they can stay resilient in a period of eventuality.
Mitigation Plan
Below are several mitigations to reduce the risk of compromise by APTs and ransomware attacks. These approaches are classified into people, processes and technology.
People –
- Implement a user training program and simulated attacks for spear phishing.
- Technical capacity building for IT team to prepare them for basic Incident Handling.
Processes –
- Filter network traffic
- Update software not limited to operating systems, but also applications and firmware on network devices, virtualization platforms
- Limit access to resources over networks, especially by restricting RDP
- Implement unauthorized execution prevention by whitelisting, disabling macros,
- Implement and ensure robust network segmentation between networks
- Implement regular data backup procedures
- Ensure user and process accounts are limited through account use policies, user account control, and privileged account management
Technology –
- Enable strong spam filters to prevent phishing emails from reaching end users.
- Set EDR/antimalware programs to conduct regular scans
- Require multi-factor authentication implementation for access!
- Enable visibility into endpoints and networks through the use of SIEM/SOAR tools.
For your holistic security operation activities, you can reach out to CyberPlural. #BeProactive Now!

Leave a Reply